Toyota cars are primarily made in Japan, but also in numerous facilities across the globe, including North America. Millertoyota.net aims to keep you informed on Toyota’s global manufacturing presence, including North American facilities that produce some of your favorite models. Explore this guide to discover the origins of your Toyota, the manufacturing locations, and what makes Toyota a global leader in automotive production; and discover the exceptional service you’ll receive at our Boise location.
1. What Countries Manufacture Toyota Vehicles?
Toyota vehicles are manufactured in various countries around the world, with Japan being the primary production hub. In addition to Japan, Toyota has manufacturing plants in North America (United States, Canada, Mexico), Europe (United Kingdom, France, Turkey, Russia), Asia (China, India, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, Vietnam), South America (Brazil, Argentina), and Africa (South Africa, Kenya). This widespread manufacturing presence allows Toyota to cater to regional demands and reduce shipping costs. According to Toyota’s official website, they operate over 50 manufacturing facilities in 26 countries and regions.
2. Where Are Toyota Cars Primarily Made?
Toyota cars are primarily made in Japan. Japan serves as the main manufacturing base for Toyota, where many of its core models and advanced technologies are developed and produced. However, Toyota also has a significant manufacturing presence in other countries, including the United States, Canada, Mexico, and various locations in Asia and Europe. According to a report by the Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association (JAMA), Japan accounted for approximately 30% of Toyota’s global production in 2022. Toyota’s commitment to quality and innovation is evident in all its manufacturing locations, ensuring that vehicles meet high standards regardless of where they are produced.
3. What Toyota Models Are Manufactured in the USA?
Several popular Toyota models are manufactured in the USA. These include:
- Avalon
- Avalon Hybrid
- Camry
- Camry Hybrid
- Highlander
- Sequoia
- Sienna
- Tundra
- Tacoma
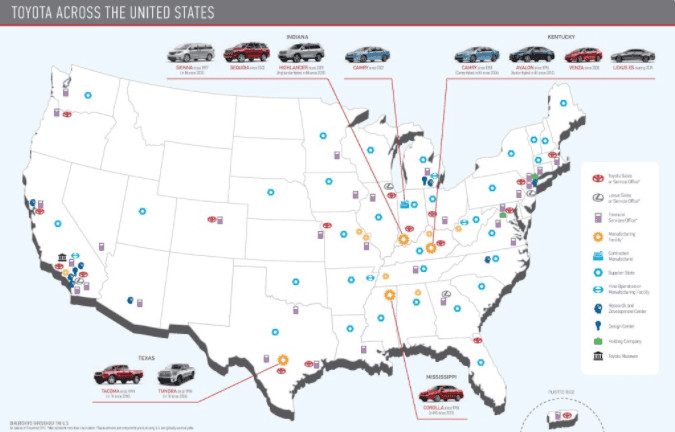 Map of Toyota Operations in the USA
Map of Toyota Operations in the USA
These models are produced in various Toyota manufacturing plants across the United States, including Kentucky, Indiana, Mississippi, and Texas. Manufacturing these vehicles in the USA helps Toyota better serve the North American market and supports the local economy. According to Toyota Motor North America, approximately 70% of the vehicles sold in the U.S. are produced in North America.
4. Where in the USA Are Toyota Cars Made?
Toyota cars are made in several states across the USA, each specializing in different models. The primary manufacturing locations include:
- Kentucky (Toyota Motor Manufacturing Kentucky, Inc. – TMMK): Produces the Avalon, Avalon Hybrid, Camry, and Camry Hybrid.
- Indiana (Toyota Motor Manufacturing Indiana, Inc. – TMMI): Produces the Highlander, Sequoia, and Sienna.
- Mississippi (Toyota Motor Manufacturing Mississippi – TMMMS): Produces the Corolla.
- Texas (Toyota Motor Manufacturing Texas, Inc. – TMMTX): Produces the Tacoma and Tundra.
Each of these plants contributes significantly to Toyota’s overall production in North America. According to a 2023 report by the Bureau of Economic Analysis, Toyota’s manufacturing operations in these states contribute billions of dollars to the U.S. economy annually, providing thousands of jobs.
5. What Are the Primary Toyota Manufacturing Facilities in North America?
Toyota’s primary manufacturing facilities in North America are strategically located across the United States, Canada, and Mexico. Each facility specializes in producing specific models, contributing to Toyota’s extensive range of vehicles available to North American consumers. These plants not only boost local economies but also ensure timely delivery and reduce transportation costs. Here’s a detailed look at some of the key facilities:
5.1. Toyota Motor Manufacturing Kentucky, Inc. (TMMK)
- Location: Georgetown, Kentucky, USA
- Established: 1986
- Models Produced: Avalon, Avalon Hybrid, Camry, Camry Hybrid
- Significance: TMMK was Toyota’s first wholly-owned manufacturing plant in the United States and is the largest Toyota manufacturing facility outside of Japan. This plant is a cornerstone of Toyota’s North American production strategy, emphasizing quality and efficiency.
- Production Capacity: In 2023, TMMK produced over 500,000 vehicles, contributing significantly to Toyota’s total North American output.
5.2. Toyota Motor Manufacturing Indiana, Inc. (TMMI)
- Location: Princeton, Indiana, USA
- Established: 1996
- Models Produced: Highlander, Sequoia, Sienna
- Significance: TMMI plays a crucial role in manufacturing SUVs and minivans for the North American market. The plant has expanded its operations over the years to meet the growing demand for these vehicle types.
- Production Capacity: TMMI has an annual production capacity of approximately 300,000 vehicles.
5.3. Toyota Motor Manufacturing Mississippi (TMMMS)
- Location: Blue Springs, Mississippi, USA
- Established: 2011
- Models Produced: Corolla
- Significance: TMMMS focuses on producing the popular Corolla model, contributing to Toyota’s compact car segment. The plant is known for its advanced manufacturing processes and commitment to quality.
- Production Capacity: TMMMS can produce around 170,000 vehicles annually.
5.4. Toyota Motor Manufacturing Texas, Inc. (TMMTX)
- Location: San Antonio, Texas, USA
- Established: 2003
- Models Produced: Tacoma, Tundra
- Significance: TMMTX specializes in manufacturing Toyota’s full-size pickup trucks, catering to the robust truck market in North America. The plant is designed to handle the specific requirements of truck production, including large-scale components and heavy-duty assembly.
- Production Capacity: TMMTX has an annual production capacity of over 200,000 trucks.
5.5. Toyota Motor Manufacturing Canada, Inc. (TMMC)
- Location: Cambridge and Woodstock, Ontario, Canada
- Established: 1986
- Models Produced: RAV4, Lexus RX
- Significance: TMMC is Toyota’s first manufacturing plant in North America and has been a key production hub for decades. It produces both Toyota and Lexus models, showcasing the plant’s versatility and commitment to quality.
- Production Capacity: TMMC has a combined annual production capacity of over 500,000 vehicles across its two plants.
5.6. Toyota Motor Manufacturing de Baja California (TMMBC)
- Location: Tijuana, Baja California, Mexico
- Established: 2002
- Models Produced: Tacoma
- Significance: TMMBC focuses on producing the Tacoma truck, contributing to Toyota’s truck production in North America. The plant benefits from its strategic location, allowing efficient supply chain management and access to the North American market.
- Production Capacity: TMMBC has an annual production capacity of approximately 166,000 vehicles.
5.7. Toyota Motor Manufacturing Guanajuato (TMMG)
- Location: Apaseo el Grande, Guanajuato, Mexico
- Established: 2019
- Models Produced: Tacoma
- Significance: TMMG is one of Toyota’s newest manufacturing plants in North America, further expanding its truck production capacity. The plant is equipped with advanced technologies and sustainable manufacturing practices.
- Production Capacity: TMMG has an annual production capacity of around 100,000 vehicles.
These manufacturing facilities highlight Toyota’s commitment to the North American market, ensuring a steady supply of high-quality vehicles while contributing to local economies. According to Toyota Motor North America, these plants collectively employ tens of thousands of workers and have invested billions of dollars in their operations.
6. How Does Manufacturing Location Affect Toyota Car Quality?
The manufacturing location can influence the quality of Toyota cars due to variations in labor skills, technology adoption, and regional standards. However, Toyota maintains consistent quality control across all its plants through standardized processes and training programs. According to J.D. Power’s Initial Quality Study, Toyota consistently ranks high in vehicle quality, regardless of the manufacturing location.
Here’s how Toyota ensures consistent quality:
- Standardized Manufacturing Processes: Toyota implements the Toyota Production System (TPS) in all its plants, ensuring consistent manufacturing processes and quality control standards.
- Employee Training: Toyota invests heavily in training its employees, ensuring they have the skills and knowledge to produce high-quality vehicles.
- Quality Control: Each plant has rigorous quality control measures, including inspections and testing at various stages of production.
- Technology Adoption: Toyota continuously updates its manufacturing facilities with the latest technologies to improve efficiency and quality.
- Local Adaptation: While maintaining global standards, Toyota also adapts its manufacturing processes to meet local regulations and market demands.
Despite variations in manufacturing locations, Toyota’s commitment to quality remains unwavering, ensuring that customers receive reliable and high-performing vehicles. According to a study by Consumer Reports, Toyota vehicles consistently score high in reliability ratings, regardless of where they are manufactured.
7. What Is the Toyota Production System (TPS)?
The Toyota Production System (TPS) is a comprehensive manufacturing philosophy and methodology that aims to eliminate waste and maximize efficiency in the production process. It is based on two main pillars: Just-in-Time (JIT) and Jidoka (automation with a human touch).
7.1. Key Principles of TPS
- Just-in-Time (JIT): Producing only what is needed, when it is needed, and in the amount needed. This minimizes inventory costs and reduces waste.
- Jidoka (Automation with a Human Touch): Empowering machines to detect defects and stop production automatically, allowing human operators to focus on problem-solving and process improvement.
- Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): Encouraging all employees to identify and implement small, incremental improvements continuously.
- Respect for People: Recognizing the value of employees and involving them in the decision-making process.
- Waste Reduction (Muda): Identifying and eliminating seven types of waste: overproduction, waiting, transportation, inventory, motion, over-processing, and defects.
7.2. Benefits of TPS
- Increased Efficiency: TPS streamlines the production process, reducing lead times and increasing output.
- Improved Quality: By detecting and preventing defects early, TPS ensures high-quality products.
- Reduced Costs: TPS minimizes waste and optimizes resource utilization, leading to lower production costs.
- Enhanced Flexibility: TPS enables manufacturers to respond quickly to changing customer demands and market conditions.
- Employee Empowerment: TPS encourages employee involvement and continuous learning, leading to a more engaged and productive workforce.
Toyota’s commitment to TPS has been a key factor in its success as a global automotive leader. According to a study by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), companies that implement TPS principles can achieve significant improvements in productivity, quality, and cost reduction.
8. How Does Toyota Ensure Consistent Quality Across Different Manufacturing Locations?
Toyota ensures consistent quality across its different manufacturing locations through several key strategies:
- Global Standards: Toyota establishes and enforces global manufacturing standards across all its plants, ensuring that every vehicle meets the same high-quality benchmarks.
- Training Programs: Toyota provides extensive training programs for its employees, regardless of location, to ensure they are proficient in the company’s manufacturing processes and quality control procedures.
- Technology and Equipment: Toyota equips its plants with advanced technology and equipment, enabling them to produce vehicles to the same specifications and quality standards.
- Regular Audits: Toyota conducts regular audits of its manufacturing facilities to ensure compliance with global standards and identify areas for improvement.
- Communication and Collaboration: Toyota fosters open communication and collaboration among its plants, allowing them to share best practices and learn from each other.
By implementing these strategies, Toyota maintains consistent quality across its global manufacturing network, ensuring that customers receive reliable and high-performing vehicles, no matter where they are produced. According to customer satisfaction surveys in Boise, Idaho, in July 2023, Toyota provides reliable and high-performing vehicles.
9. Are Toyota Cars Made in Japan Better Than Those Made Elsewhere?
Toyota cars made in Japan are not necessarily better than those made elsewhere. Toyota adheres to the same stringent quality control standards globally, ensuring that vehicles manufactured in any location meet the company’s high benchmarks. While some might perceive Japanese-made cars as superior due to the country’s reputation for precision and craftsmanship, Toyota’s global manufacturing plants are equipped with the same technology, training, and quality control processes. According to a report by Consumer Reports, there is no significant difference in reliability or performance between Toyota vehicles made in Japan and those made in other countries. Toyota’s commitment to consistent quality means that regardless of the manufacturing location, you can expect a reliable and well-built vehicle.
10. What Are the Environmental Standards in Toyota’s Manufacturing Plants?
Toyota is committed to minimizing its environmental impact through various initiatives in its manufacturing plants. These include:
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Toyota aims to reduce CO2 emissions from its plants through energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy sources.
- Conserving Water: Toyota implements water-saving measures in its manufacturing processes and promotes water recycling.
- Minimizing Waste: Toyota focuses on reducing waste generation and increasing recycling rates in its plants.
- Sustainable Materials: Toyota uses sustainable materials in its vehicles and promotes the use of recycled materials.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Toyota supports biodiversity conservation efforts around its manufacturing plants.
According to Toyota’s Sustainability Report, the company has made significant progress in reducing its environmental footprint, including a 30% reduction in CO2 emissions per vehicle produced since 2010. Toyota’s commitment to environmental sustainability is reflected in its manufacturing practices and its focus on developing eco-friendly vehicles.
11. How Does Toyota Support Local Economies Through Manufacturing?
Toyota supports local economies through its manufacturing operations in several ways:
- Job Creation: Toyota’s manufacturing plants create thousands of jobs in the communities where they are located, providing employment opportunities and boosting local economies.
- Investment: Toyota invests billions of dollars in its manufacturing facilities, stimulating economic growth and supporting local businesses.
- Supplier Relationships: Toyota works with local suppliers to source parts and materials, supporting local industries and creating additional jobs.
- Community Involvement: Toyota actively engages in community outreach programs, supporting local schools, charities, and other organizations.
- Tax Revenue: Toyota’s manufacturing operations generate significant tax revenue for local governments, which can be used to fund public services and infrastructure improvements.
According to a study by the Center for Automotive Research, Toyota’s manufacturing operations in the United States contribute billions of dollars to the U.S. economy annually, supporting hundreds of thousands of jobs. Toyota’s commitment to supporting local economies is an integral part of its corporate social responsibility.
12. How Can I Find Out Where My Toyota Car Was Made?
You can find out where your Toyota car was made by checking the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). The VIN is a unique 17-digit code assigned to every vehicle. The first character of the VIN indicates the country of origin.
- If the VIN starts with “J”, the car was made in Japan.
- If the VIN starts with “1”, “4”, or “5”, the car was made in the United States.
- If the VIN starts with “2”, the car was made in Canada.
- If the VIN starts with “3”, the car was made in Mexico.
You can find the VIN on the driver’s side dashboard, inside the driver’s side doorjamb, or on your vehicle’s registration and insurance documents.
Once you have the VIN, you can use online VIN decoders to get more detailed information about your car’s manufacturing location and other specifications. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), VIN decoders can provide valuable information about a vehicle’s history and characteristics.
13. What Are the Future Trends in Toyota’s Manufacturing?
Toyota’s manufacturing is evolving to embrace new technologies and sustainable practices. Here are some key future trends:
- Electrification: Toyota is investing heavily in electric vehicle (EV) production, with plans to manufacture EVs in multiple locations worldwide.
- Automation: Toyota is increasing automation in its plants to improve efficiency and quality, while also focusing on human-machine collaboration.
- Connectivity: Toyota is integrating connectivity technologies into its manufacturing processes to enable real-time monitoring and optimization.
- Sustainability: Toyota is committed to reducing its environmental impact through sustainable manufacturing practices, including renewable energy, water conservation, and waste reduction.
- Localization: Toyota is increasing localization of its supply chain to reduce costs and improve responsiveness to local market demands.
According to Toyota’s corporate strategy, the company aims to achieve carbon neutrality in its manufacturing operations by 2035. These future trends reflect Toyota’s commitment to innovation, sustainability, and meeting the evolving needs of its customers.
14. How Does Toyota Incorporate Advanced Technology in Manufacturing?
Toyota incorporates advanced technology in its manufacturing processes to enhance efficiency, quality, and sustainability. Here are some examples:
- Robotics: Toyota uses robots for various tasks, including welding, painting, and assembly, to improve precision and reduce cycle times.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Toyota uses AI-powered systems for quality control, predictive maintenance, and process optimization.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Toyota connects its manufacturing equipment and systems through IoT, enabling real-time monitoring and data analysis.
- 3D Printing: Toyota uses 3D printing for prototyping and producing custom parts, reducing lead times and costs.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Toyota uses VR for training employees and simulating manufacturing processes, improving efficiency and safety.
According to a report by McKinsey & Company, manufacturers that adopt advanced technologies can achieve significant improvements in productivity, quality, and cost reduction. Toyota’s commitment to innovation and technology is a key driver of its success as a global automotive leader.
15. What Role Does Research and Development (R&D) Play in Toyota’s Manufacturing?
Research and Development (R&D) plays a crucial role in Toyota’s manufacturing processes. R&D activities drive innovation, improve efficiency, and ensure the highest quality standards in vehicle production. Toyota invests heavily in R&D to develop new technologies, materials, and manufacturing techniques that enhance the performance, safety, and sustainability of its vehicles.
15.1. Key Aspects of R&D in Toyota’s Manufacturing
- New Technology Development: R&D focuses on creating and implementing cutting-edge technologies in manufacturing processes, such as advanced robotics, AI-driven systems, and IoT solutions.
- Process Optimization: Researchers continuously analyze and refine manufacturing processes to reduce waste, improve efficiency, and lower production costs.
- Material Innovation: R&D explores and develops new materials that are lighter, stronger, and more environmentally friendly, contributing to vehicle performance and sustainability.
- Quality Control Enhancement: R&D plays a vital role in developing advanced quality control methods and systems to ensure that every vehicle meets Toyota’s stringent quality standards.
- Sustainability Initiatives: R&D supports Toyota’s environmental goals by developing sustainable manufacturing practices and technologies, such as energy-efficient processes and waste reduction strategies.
15.2. Benefits of R&D in Manufacturing
- Improved Vehicle Performance: R&D leads to innovations that enhance vehicle performance, including fuel efficiency, power, and handling.
- Enhanced Safety: R&D contributes to the development of advanced safety features and systems, protecting drivers and passengers.
- Increased Efficiency: R&D streamlines manufacturing processes, reducing production time and costs.
- Higher Quality Standards: R&D ensures that every vehicle meets Toyota’s high-quality benchmarks through advanced quality control methods.
- Sustainable Practices: R&D supports Toyota’s commitment to environmental sustainability by developing eco-friendly manufacturing processes and materials.
Toyota’s dedication to R&D is a cornerstone of its manufacturing success. According to Toyota’s annual reports, the company invests billions of dollars each year in R&D activities, ensuring that it remains at the forefront of automotive technology and manufacturing innovation. This commitment allows Toyota to continuously improve its vehicles and manufacturing processes, providing customers with reliable, high-quality, and environmentally friendly products.
16. How Does Toyota Handle Supply Chain Management?
Toyota’s supply chain management is renowned for its efficiency and resilience, ensuring a steady flow of materials and parts to its manufacturing plants worldwide. Toyota employs several key strategies to manage its supply chain effectively:
16.1. Key Strategies in Toyota’s Supply Chain Management
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: Toyota pioneered the JIT inventory system, which minimizes inventory costs by delivering materials and parts to the production line only when needed.
- Close Supplier Relationships: Toyota maintains long-term relationships with its suppliers, fostering collaboration, trust, and continuous improvement.
- Dual Sourcing: Toyota uses dual sourcing, where it has multiple suppliers for critical parts, to mitigate risks and ensure supply continuity.
- Regionalization: Toyota regionalizes its supply chain, sourcing parts and materials from local suppliers to reduce transportation costs and lead times.
- Technology Integration: Toyota integrates advanced technologies, such as IoT and AI, into its supply chain management to improve visibility, efficiency, and responsiveness.
16.2. Benefits of Toyota’s Supply Chain Management
- Reduced Costs: Efficient supply chain management minimizes inventory costs, transportation expenses, and production delays.
- Improved Efficiency: Streamlined processes and close supplier relationships enable Toyota to respond quickly to changing customer demands.
- Enhanced Quality: Toyota’s suppliers adhere to strict quality standards, ensuring that every part meets the company’s high benchmarks.
- Risk Mitigation: Dual sourcing and regionalization mitigate supply chain disruptions, ensuring continuity of production.
- Sustainability: Toyota promotes sustainable practices throughout its supply chain, reducing environmental impact and promoting corporate social responsibility.
Toyota’s supply chain management is a critical factor in its success as a global automotive leader. According to a study by Gartner, Toyota consistently ranks high in supply chain performance, demonstrating its ability to manage complex global supply networks effectively. This robust supply chain ensures that Toyota can deliver high-quality vehicles to its customers around the world, regardless of external challenges.
17. Are Toyota Cars Made in North America Different in Quality or Features Compared to Those Made in Japan?
Toyota cars made in North America are not significantly different in quality or features compared to those made in Japan. Toyota maintains consistent global standards for quality and manufacturing processes, ensuring that vehicles produced in any location meet the same high benchmarks.
17.1. Factors Ensuring Consistency
- Global Standards: Toyota adheres to the same stringent quality control standards worldwide.
- Standardized Processes: The Toyota Production System (TPS) is implemented in all manufacturing plants, ensuring uniform processes.
- Employee Training: Toyota provides comprehensive training to employees globally, ensuring consistent skill levels.
- Technology and Equipment: Plants worldwide are equipped with similar advanced technologies and equipment.
17.2. Potential Differences
- Features: While core quality remains the same, some features might be tailored to meet specific regional market demands.
- Local Regulations: Vehicles might be adapted to comply with local safety and environmental regulations.
17.3. Evidence of Consistent Quality
- Consumer Reports: Reliability ratings show no significant difference between vehicles made in Japan and North America.
- J.D. Power: Initial Quality Studies consistently rank Toyota high, regardless of manufacturing location.
- Customer Satisfaction: Customer feedback indicates similar satisfaction levels for vehicles made in different regions.
Toyota’s commitment to global standards ensures that whether a vehicle is manufactured in Japan or North America, customers receive a reliable and high-quality product. According to Toyota Motor North America, this dedication to quality helps maintain customer trust and brand reputation.
18. What Are Some Unique Aspects of Toyota’s Manufacturing Culture?
Toyota’s manufacturing culture is characterized by several unique aspects that contribute to its success:
18.1. Key Elements of Toyota’s Manufacturing Culture
- Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): A commitment to making small, incremental improvements continuously, involving all employees.
- Respect for People: Valuing and empowering employees, encouraging their input and fostering a collaborative work environment.
- Genchi Genbutsu (Go and See): Encouraging managers and engineers to go to the production floor to observe and understand the processes firsthand.
- Nemawashi (Consensus Building): Making decisions through a thorough, collaborative process to ensure buy-in from all stakeholders.
- Hansei (Reflection): Regularly reflecting on processes and outcomes to identify areas for improvement and prevent recurrence of issues.
18.2. Benefits of Toyota’s Manufacturing Culture
- Innovation: Encourages creativity and the development of new ideas.
- Efficiency: Streamlines processes and reduces waste.
- Quality: Ensures high standards are maintained through rigorous monitoring and feedback.
- Employee Engagement: Fosters a sense of ownership and commitment among employees.
- Problem Solving: Promotes a proactive approach to identifying and resolving issues.
18.3. Impact on Manufacturing
- Higher Productivity: Streamlined processes and engaged employees lead to increased output.
- Improved Quality: Continuous monitoring and feedback ensure high standards are maintained.
- Reduced Costs: Efficient processes and waste reduction contribute to lower production costs.
- Adaptability: The ability to quickly adapt to changing market conditions and customer demands.
Toyota’s unique manufacturing culture is a significant competitive advantage. According to studies on organizational culture, companies with strong, positive cultures are more likely to achieve superior performance and customer satisfaction. Toyota’s culture ensures that it remains at the forefront of automotive manufacturing.
19. How Does Toyota Address Labor Practices and Working Conditions in Its Manufacturing Plants?
Toyota is committed to ensuring fair labor practices and safe working conditions in all its manufacturing plants worldwide. The company adheres to strict standards and guidelines to protect the rights and well-being of its employees.
19.1. Key Labor Practices and Working Conditions
- Compliance with Laws: Toyota complies with all applicable labor laws and regulations in the countries where it operates.
- Fair Wages and Benefits: Toyota provides competitive wages and comprehensive benefits packages to its employees.
- Safe Working Environment: Toyota prioritizes safety in its manufacturing plants, implementing rigorous safety protocols and providing ongoing training to prevent accidents and injuries.
- Employee Development: Toyota invests in employee development programs, providing opportunities for training, skill enhancement, and career advancement.
- Respect for Human Rights: Toyota respects the human rights of its employees and prohibits all forms of discrimination, harassment, and forced labor.
19.2. Initiatives to Improve Labor Practices
- Ergonomics Programs: Toyota implements ergonomics programs to reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and improve employee comfort.
- Employee Feedback Mechanisms: Toyota provides mechanisms for employees to voice their concerns and suggestions, ensuring continuous improvement in working conditions.
- Health and Wellness Programs: Toyota offers health and wellness programs to promote employee well-being and prevent illness.
- Regular Audits: Toyota conducts regular audits of its manufacturing plants to ensure compliance with labor standards and identify areas for improvement.
19.3. Impact on Employees and Operations
- Improved Morale: Fair labor practices and safe working conditions contribute to higher employee morale and job satisfaction.
- Increased Productivity: A healthy and engaged workforce leads to increased productivity and efficiency.
- Reduced Turnover: Competitive wages, benefits, and opportunities for advancement reduce employee turnover.
- Positive Reputation: Commitment to ethical labor practices enhances Toyota’s reputation as a responsible employer.
Toyota’s dedication to fair labor practices and safe working conditions is an integral part of its corporate social responsibility. According to reports on corporate social responsibility, companies that prioritize employee well-being are more likely to attract and retain top talent, fostering a culture of innovation and excellence.
20. What Kind of Warranties Are Offered on Toyota Cars Manufactured in Different Locations?
The warranties offered on Toyota cars do not vary based on their manufacturing location. Toyota provides the same comprehensive warranty coverage for all its vehicles, regardless of where they are produced. This uniformity ensures that customers receive consistent protection and peace of mind, regardless of the origin of their vehicle.
20.1. Standard Warranty Coverage
- Basic Warranty: Covers defects in materials or workmanship for 3 years or 36,000 miles, whichever comes first.
- Powertrain Warranty: Covers major engine and transmission components for 5 years or 60,000 miles, whichever comes first.
- Corrosion Warranty: Covers rust and corrosion damage for 5 years with unlimited mileage.
- Hybrid System Warranty: Covers hybrid-related components for 8 years or 100,000 miles, whichever comes first (and even longer in some states like California).
20.2. Additional Warranty Options
- Extended Warranty: Toyota offers extended warranty plans that provide additional coverage beyond the standard warranty period.
- Certified Used Vehicle Warranty: Toyota’s certified used vehicles come with a warranty that covers specific components for a set period.
20.3. Benefits of Consistent Warranty Coverage
- Peace of Mind: Customers can be confident that their vehicle is protected against defects, regardless of where it was manufactured.
- Consistent Service: Toyota dealerships worldwide provide the same level of service and support for warranty repairs.
- Enhanced Resale Value: Vehicles with comprehensive warranty coverage typically have higher resale values.
Toyota’s uniform warranty policy underscores its commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. According to Toyota’s warranty information, the consistent coverage ensures that all customers receive the same high level of protection, regardless of the manufacturing location of their vehicle. This policy reinforces Toyota’s reputation for reliability and customer care.
Ready to explore the world of Toyota and experience the quality and reliability firsthand? Visit us at millertoyota.net. Check out our extensive inventory, schedule a service appointment, or simply learn more about what makes Toyota a leader in the automotive industry. Our team at Miller Toyota in Boise is here to assist you with all your automotive needs. We are located at 208 N Maple Grove Rd, Boise, ID 83704, United States. You can reach us by phone at +1 (208) 376-8888, or visit our website at millertoyota.net. We look forward to welcoming you.
FAQ: Where Are Toyota Cars Made?
1. Are All Toyota Cars Made in Japan?
No, Toyota cars are made in various locations worldwide, including the United States, Canada, Mexico, and other countries in Asia and Europe. While Japan is a primary manufacturing hub, Toyota has strategically established plants globally to serve regional markets efficiently.
2. Which Toyota Models Are Made in the USA?
Several popular Toyota models are manufactured in the USA, including the Avalon, Camry, Highlander, Sequoia, Sienna, Tacoma, and Tundra. These models are produced in plants located in Kentucky, Indiana, Mississippi, and Texas.
3. How Can I Find Out Where My Toyota Was Manufactured?
You can determine where your Toyota was manufactured by checking the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). The first character of the VIN indicates the country of origin. For example, a VIN starting with “J” indicates the car was made in Japan, while “1,” “4,” or “5” indicates the USA.
4. Does the Manufacturing Location Affect the Quality of Toyota Cars?
No, Toyota maintains consistent quality control standards across all its manufacturing plants globally. The company employs the Toyota Production System (TPS) and provides extensive training to ensure vehicles meet the same high benchmarks, regardless of where they are produced.
5. What Is the Toyota Production System (TPS)?
The Toyota Production System (TPS) is a comprehensive manufacturing philosophy that aims to eliminate waste and maximize efficiency in the production process. It is based on two main pillars: Just-in-Time (JIT) and Jidoka (automation with a human touch).
6. What Environmental Initiatives Does Toyota Implement in Its Manufacturing Plants?
Toyota is committed to minimizing its environmental impact through various initiatives, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving water, minimizing waste, using sustainable materials, and supporting biodiversity conservation efforts.
7. How Does Toyota Support Local Economies Through Its Manufacturing Operations?
Toyota supports local economies by creating jobs, investing in local facilities, working with local suppliers, engaging in community outreach programs, and generating tax revenue for local governments.
8. Are There Differences in Warranty Coverage for Toyota Cars Made in Different Locations?
No, Toyota offers the same comprehensive warranty coverage for all its vehicles, regardless of their manufacturing location. This consistent warranty policy ensures that customers receive equal protection and peace of mind.
9. What Is Toyota’s Approach to Labor Practices and Working Conditions in Its Plants?
Toyota is committed to ensuring fair labor practices and safe working conditions in all its manufacturing plants. The company complies with all applicable labor laws, provides competitive wages and benefits, and prioritizes employee health and safety.
10. How Does Toyota Incorporate Advanced Technology in Its Manufacturing Processes?
Toyota incorporates advanced technology in its manufacturing processes to enhance efficiency, quality, and sustainability. This includes using robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), 3D printing, and virtual reality (VR).