Who Makes Toyota Vehicles, and where are they manufactured? Toyota vehicles are made by Toyota Motor Corporation, a global automotive manufacturer headquartered in Japan, with numerous manufacturing facilities located around the world including North America, specifically the United States. MillerToyota.net is your go-to resource for finding the perfect Toyota and ensuring it receives top-notch service. Uncover crucial facts about the company behind this brand.
1. Who is the Primary Manufacturer of Toyota Vehicles?
Toyota Motor Corporation is the primary manufacturer of Toyota vehicles. Established in 1937 by Kiichiro Toyoda, Toyota Motor Corporation has grown into one of the world’s leading automotive manufacturers, renowned for its commitment to quality, reliability, and innovation.
1.1. Historical Context of Toyota Motor Corporation
The company’s roots can be traced back to Toyoda Automatic Loom Works, a textile machinery manufacturer founded by Kiichiro Toyoda’s father, Sakichi Toyoda. Kiichiro’s passion for automobiles led him to explore automotive manufacturing, and in 1937, he established Toyota Motor Corporation as a separate entity.
1.2. Global Presence of Toyota
Today, Toyota has a global presence, with manufacturing plants, sales offices, and research and development centers in numerous countries. The company’s vehicles are sold in over 170 countries and regions worldwide. Toyota is committed to sustainable mobility, pioneering hybrid and electric vehicle technology.
1.3. How Toyota ensures quality and reliability?
Toyota focuses on quality and reliability by implementing rigorous manufacturing processes, utilizing advanced technologies, and adhering to strict quality control standards. The company’s commitment to continuous improvement, or “Kaizen,” ensures that every vehicle meets the highest standards of performance and durability.
2. Where are Toyota Vehicles Manufactured Primarily?
Toyota vehicles are manufactured primarily in Japan and North America, with additional manufacturing facilities located in Asia, Europe, and South America. These facilities adhere to Toyota’s strict quality control standards to ensure every vehicle meets the highest levels of performance and reliability.
2.1. Manufacturing Plants in Japan
Toyota has numerous manufacturing plants in Japan, including its headquarters in Toyota City, Aichi Prefecture. These plants produce a wide range of Toyota vehicles, from compact cars to luxury sedans, for both domestic and international markets.
2.2. Manufacturing Plants in North America
Toyota has invested heavily in North American manufacturing facilities, including plants in the United States, Canada, and Mexico. These plants produce popular Toyota models, such as the Camry, Corolla, Tacoma, and Tundra, specifically tailored to the needs and preferences of North American consumers. As of this writing, Toyota manufactures 12 customer favorite vehicles in their North American facilities. Among the list of the vehicles manufactured in these plants include Avalon, Corolla, Camry, Highlander, RAV4, Matrix, Sienna, Tundra, Sequoia, Tacoma, Venaz, and the Lexus RX350. Their car manufacturing facilities are based in locations such as Kentucky, Indiana, Canada, Mississippi, California, and Texas.
2.3. Other Global Manufacturing Locations
In addition to Japan and North America, Toyota has manufacturing facilities in other regions around the world, including Asia, Europe, and South America. These plants produce vehicles for local markets and export to other countries.
3. What Specific Toyota Models are Manufactured in the USA?
Several popular Toyota models are manufactured in the USA, including the Camry, Avalon, Tundra, Tacoma, Sequoia, and Highlander. These models are produced in Toyota’s manufacturing plants located in Kentucky, Indiana, Mississippi, and Texas, providing jobs and supporting the American economy.
3.1. Toyota Motor Manufacturing Kentucky, Inc. (TMMK)
Established in 1986, Toyota Motor Manufacturing, Kentucky, Inc. (TMMK) was the first wholly owned US-based Toyota manufacturing plant. To date, it is the largest manufacturing facility located outside Japan. The models that are being manufactured in this plant include the 2013 Avalon, Avalon Hybrid Camry, Camry Hybrid, and Venza. The plant was able to manufacture 504,213 vehicles in 2013.
3.2. Toyota Motor Manufacturing Indiana, Inc. (TMMI)
Located in Gibson County, Indiana, the Toyota Motor Manufacturing Indiana Inc. (TMMI) was established in 1996 solely to manufacture full-size pickup trucks for the American market. To date, the facility has moved to manufacturing SUVs such as the Highlander, Sequoia, and Sienna. In 2013, the facility was able to produce up to 299,820 vehicles.
3.3. Toyota Motor Manufacturing Mississippi (TMMMS)
Located in Blue Springs, Mississippi, the TMMMS was originally planned to manufacture the Toyota Highlander in 2010. Unfortunately, the car manufacturer decided to move production to the Indiana plant. In 2011, the facility was opened to produce the best selling Corolla. In 2013 alone, the facility was able to produce 158,647 vehicles.
3.4. Toyota Motor Manufacturing Texas, Inc. (TMMTX)
In 2003, Toyota was able to acquire a new facility in San Antonio, Texas. This facility focuses in manufacturing Toyota full-size pickup trucks like the Tacoma and Tundra. In 2013, they were able to produce 228,983 vehicles.
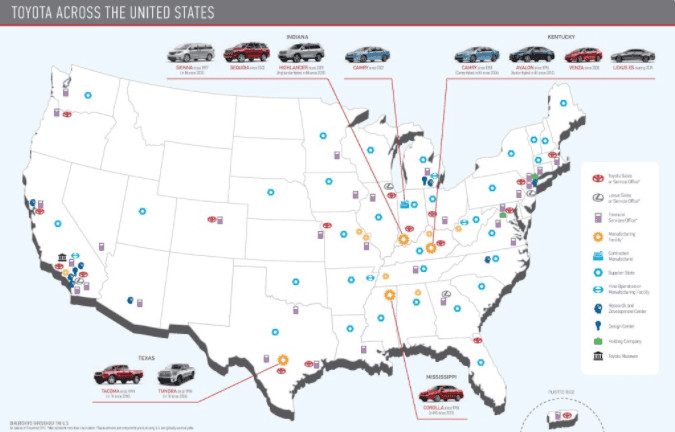 Map of Toyota Operations in the USA
Map of Toyota Operations in the USA
Toyota manufacturing facilities in the USA
4. How Does Toyota Ensure Quality Control in Its Manufacturing Plants?
Toyota ensures quality control in its manufacturing plants through the Toyota Production System (TPS), a comprehensive set of principles and practices focused on eliminating waste, improving efficiency, and ensuring quality at every stage of the manufacturing process. The Toyota Production System (TPS) is a comprehensive approach that ensures waste reduction, efficiency improvement, and superior quality at every manufacturing stage.
4.1. The Toyota Production System (TPS)
The Toyota Production System (TPS) is a management philosophy and set of practices that Toyota developed to improve efficiency, eliminate waste, and ensure quality in its manufacturing operations. The TPS emphasizes continuous improvement, respect for people, and a focus on the customer.
4.2. Key Principles of TPS
Some of the key principles of TPS include:
- Just-in-Time (JIT): Producing only what is needed, when it is needed, and in the quantity needed.
- Jidoka (Autonomation): Designing equipment to automatically detect defects and stop production, preventing defective products from moving further down the line.
- Kaizen (Continuous Improvement): Encouraging all employees to identify and implement small, incremental improvements to processes and products.
- Genchi Genbutsu (Go and See): Encouraging managers and engineers to go to the shop floor to observe and understand the actual conditions.
4.3. Implementation of Quality Control Measures
Toyota implements various quality control measures in its manufacturing plants, including:
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): Using statistical methods to monitor and control the manufacturing process, ensuring that it remains within acceptable limits.
- Inspection and Testing: Conducting thorough inspections and tests at various stages of the manufacturing process to identify and correct defects.
- Employee Training: Providing employees with comprehensive training on quality control procedures and techniques.
5. What is Toyota’s Commitment to Sustainable Manufacturing?
Toyota is committed to sustainable manufacturing, focusing on reducing its environmental impact through energy efficiency, waste reduction, and the use of renewable resources. This commitment reflects Toyota’s long-term vision of creating a sustainable society and minimizing its carbon footprint.
5.1. Environmental Initiatives
Toyota has implemented various environmental initiatives in its manufacturing plants, including:
- Energy Efficiency: Reducing energy consumption through the use of energy-efficient equipment, lighting, and building design.
- Waste Reduction: Minimizing waste generation through recycling, reuse, and waste reduction programs.
- Water Conservation: Conserving water through the use of water-efficient equipment and processes.
- Renewable Energy: Utilizing renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to generate electricity for its manufacturing plants.
5.2. Green Manufacturing Technologies
Toyota is also investing in green manufacturing technologies, such as:
- Waterborne Paints: Using waterborne paints, which emit fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) than solvent-based paints.
- Recycled Materials: Using recycled materials in its vehicles and manufacturing processes.
- Closed-Loop Recycling: Implementing closed-loop recycling systems, where waste materials are recycled and reused in the manufacturing process.
5.3. Environmental Certifications
Toyota’s commitment to sustainable manufacturing is demonstrated by its achievement of various environmental certifications, such as ISO 14001, which recognizes organizations that have implemented effective environmental management systems.
6. How Does Toyota Adapt Its Manufacturing Processes to Different Markets?
Toyota adapts its manufacturing processes to different markets by considering local regulations, consumer preferences, and market conditions. The company tailors its vehicle designs, features, and manufacturing processes to meet the specific needs and requirements of each market, ensuring customer satisfaction and market competitiveness.
6.1. Market Research and Analysis
Toyota conducts thorough market research and analysis to understand the needs and preferences of consumers in different markets. This research includes studying local regulations, consumer demographics, and market trends.
6.2. Vehicle Customization
Toyota customizes its vehicles to meet the specific needs and requirements of each market. This customization may include:
- Engine Options: Offering different engine options to meet local emissions standards and consumer preferences.
- Feature Packages: Providing different feature packages to cater to local tastes and preferences.
- Design Modifications: Modifying vehicle designs to meet local safety regulations and consumer preferences.
6.3. Local Sourcing
Toyota sources parts and components from local suppliers to reduce transportation costs, support local economies, and meet local content requirements. This local sourcing also helps Toyota to adapt its manufacturing processes to local conditions and regulations.
7. What Role Does Innovation Play in Toyota’s Manufacturing Processes?
Innovation plays a crucial role in Toyota’s manufacturing processes, driving efficiency, quality, and sustainability. Toyota continuously invests in research and development to develop new technologies and processes that improve its manufacturing operations and enhance the performance and reliability of its vehicles.
7.1. Research and Development
Toyota invests heavily in research and development to develop new technologies and processes that improve its manufacturing operations. This research includes:
- Advanced Materials: Developing new materials that are lighter, stronger, and more durable.
- Robotics and Automation: Implementing robotics and automation technologies to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Utilizing AI to optimize manufacturing processes and improve quality control.
7.2. New Manufacturing Technologies
Toyota is also investing in new manufacturing technologies, such as:
- 3D Printing: Using 3D printing to create prototypes and manufacture parts for its vehicles.
- Laser Welding: Utilizing laser welding to improve the strength and precision of welds.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Using VR to train employees and simulate manufacturing processes.
7.3. Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
Toyota’s commitment to continuous improvement, or “Kaizen,” encourages all employees to identify and implement small, incremental improvements to processes and products. This culture of innovation ensures that Toyota’s manufacturing processes are constantly evolving and improving.
8. How Does Toyota Train Its Manufacturing Employees?
Toyota trains its manufacturing employees through a comprehensive training program that combines classroom instruction, hands-on training, and on-the-job mentoring. This training program ensures that employees have the skills and knowledge necessary to perform their jobs safely and effectively, contributing to Toyota’s commitment to quality and efficiency.
8.1. Training Centers
Toyota operates training centers at its manufacturing plants, where employees receive classroom instruction and hands-on training on various manufacturing processes and techniques. These training centers are equipped with state-of-the-art equipment and facilities.
8.2. On-the-Job Training
In addition to classroom instruction and hands-on training, Toyota provides employees with on-the-job training, where they work alongside experienced employees and mentors to learn the ropes. This on-the-job training helps employees to develop practical skills and knowledge.
8.3. Continuous Learning
Toyota encourages its employees to engage in continuous learning and development through various programs, such as:
- Tuition Reimbursement: Providing tuition reimbursement for employees who pursue further education.
- Online Training: Offering online training courses on various topics, such as quality control, safety, and leadership.
- Mentoring Programs: Pairing employees with experienced mentors who can provide guidance and support.
9. What is Toyota’s Approach to Supply Chain Management?
Toyota’s approach to supply chain management is based on the principles of Just-in-Time (JIT) and lean manufacturing, focusing on minimizing inventory, reducing lead times, and ensuring a smooth flow of materials and information throughout the supply chain. This approach enables Toyota to respond quickly to changing market conditions and maintain a competitive advantage.
9.1. Just-in-Time (JIT) Manufacturing
Toyota’s Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing system aims to produce only what is needed, when it is needed, and in the quantity needed. This system minimizes inventory costs, reduces waste, and improves efficiency.
9.2. Supplier Relationships
Toyota maintains close relationships with its suppliers, working collaboratively to improve quality, reduce costs, and ensure a reliable supply of materials. These relationships are based on trust, transparency, and mutual benefit.
9.3. Supply Chain Visibility
Toyota utilizes advanced technology to track and monitor materials and information throughout its supply chain. This supply chain visibility enables Toyota to identify and respond quickly to potential disruptions, ensuring a smooth flow of materials and information.
10. How Does Toyota Address Labor Practices in Its Manufacturing Plants?
Toyota addresses labor practices in its manufacturing plants by adhering to strict labor standards, providing fair wages and benefits, and promoting a safe and healthy work environment. The company is committed to treating its employees with respect and dignity, ensuring their well-being and fostering a positive work culture.
10.1. Labor Standards
Toyota adheres to strict labor standards in its manufacturing plants, complying with all applicable laws and regulations. These standards cover areas such as wages, working hours, and working conditions.
10.2. Employee Benefits
Toyota provides its employees with a comprehensive package of benefits, including:
- Health Insurance: Providing health insurance coverage for employees and their families.
- Retirement Plans: Offering retirement plans, such as 401(k) plans, to help employees save for retirement.
- Paid Time Off: Providing paid time off for vacation, holidays, and sick leave.
10.3. Safety and Health
Toyota is committed to providing a safe and healthy work environment for its employees. The company implements various safety measures to prevent accidents and injuries, and it provides employees with training on safety procedures.
Seeking a trustworthy Toyota dealership in Boise offering exceptional service at competitive prices? Want to learn about available financial incentives and promotions? Visit Miller Toyota today. Our knowledgeable team is ready to offer expert advice and support!
FAQ: Who Makes Toyota Vehicles?
1. Who ultimately owns Toyota?
Toyota Motor Corporation is ultimately owned by its shareholders. These shareholders include institutional investors, individual investors, and other entities that hold shares in the company.
2. Who makes Toyota engines?
Toyota engines are primarily made by Toyota Motor Corporation in its own manufacturing plants. However, some engine components may be sourced from external suppliers.
3. Is Toyota owned by Ford?
No, Toyota is not owned by Ford. Toyota Motor Corporation is an independent company that competes with Ford Motor Company in the global automotive market.
4. Where are Toyota Tacomas made?
Toyota Tacomas are made in Toyota’s manufacturing plants in Mexico and the United States. The Toyota Motor Manufacturing, Baja California (TMMBC) plant in Baja California, Mexico, and the Toyota Motor Manufacturing Texas (TMMTX) plant in San Antonio, Texas, produce the Tacoma pickup truck.
5. Who makes Toyota transmissions?
Toyota transmissions are primarily made by Aisin Seiki Co., Ltd., a member of the Toyota Group. Aisin Seiki is a leading manufacturer of automotive components, including transmissions, brakes, and chassis systems.
6. Where is Toyota headquarters located?
Toyota’s headquarters is located in Toyota City, Aichi Prefecture, Japan. This city was formerly known as Koromo, but it was renamed Toyota City in 1959 to reflect the company’s presence and influence.
7. Are Toyota parts made in China?
While some Toyota parts may be sourced from China, Toyota also has manufacturing facilities and suppliers in many other countries around the world. Toyota’s global supply chain ensures a diverse and reliable source of parts for its vehicles.
8. Who is the CEO of Toyota?
The current CEO of Toyota Motor Corporation is Koji Sato. He assumed the position on April 1, 2023, succeeding Akio Toyoda.
9. Is Toyota reliable?
Yes, Toyota is widely regarded as one of the most reliable automotive brands. Toyota vehicles consistently rank high in reliability surveys and studies, known for their durability, longevity, and low maintenance costs.
10. What makes Toyota so special?
Toyota’s commitment to quality, reliability, and continuous improvement sets it apart from other automotive manufacturers. The Toyota Production System (TPS) and the company’s focus on customer satisfaction have contributed to its success and reputation as a leader in the automotive industry.
Ready to discover your dream Toyota, experience top-tier service, and uncover irresistible deals? Visit millertoyota.net now to browse our extensive inventory, schedule a service appointment, or get in touch with our friendly team at Miller Toyota in Boise! We are located at 208 N Maple Grove Rd, Boise, ID 83704, United States. Phone: +1 (208) 376-8888. Website: millertoyota.net.